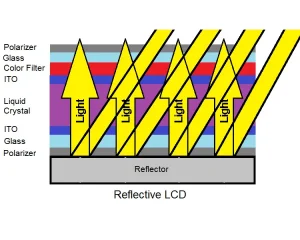
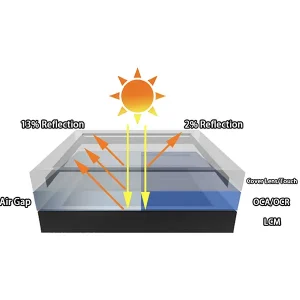
Transflective vs Reflective LCD: Which Display Technology Is Best for Outdoor Sunlight Environments?
Transflective vs Reflective LCD for Outdoor Devices As demand for outdoor displays continues to grow, including smart handheld devices, industrial terminals, smart retail systems, and outdoor instrumentation, sunlight readability has become a key design consideration....