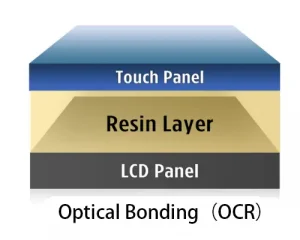
TFT LCD Water Ripple Phenomenon: Causes, Impact, and Solutions
Disclaimer:The contents of this article are purely engineering and technical reference. It is not a product specification or guarantee but a concentration on physical and optical processes of TFT LCD water ripple phenomenon. 1. What...