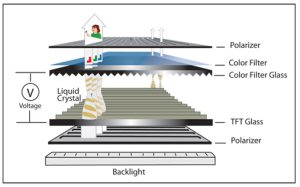
Selecting the right TFT LCD display can be challenging. These screens are widely used in automotive dashboards, industrial HMIs, outdoor terminals, and medical devices. Not every project requires the highest temperature tolerance or most advanced technology. Often, a well-chosen standard display performs just as well. Understanding your environment and requirements is the first step to selecting the right screen.
With more devices being deployed in harsh environments, knowing the difference between standard and wide temperature TFT LCDs is critical. A wrong choice can affect response time, brightness consistency, and overall system reliability.
Why Temperature Matters in TFT LCD Displays

Temperature significantly impacts display behavior. Even small environmental changes can influence performance and lifespan.
- Liquid Crystal Response: Cold temperatures increase viscosity of the liquid crystals, slowing their response. This may result in ghosting, delayed image updates, or a sluggish interface. High temperatures can degrade material stability, leading to contrast variation, image retention, and accelerated aging.
- TFT Backplane Behavior: Carrier mobility decreases in cold, limiting pixel drive. In hot conditions, threshold voltage drift, leakage currents, and long-term wear can occur, affecting image quality over time.
- Backlight Efficiency: LED backlights lose efficiency in cold and decay faster in heat. Without proper thermal management, brightness may drop unevenly, impacting readability.
- System Reliability: TFT LCD performance directly affects connected systems. In automotive dashboards or industrial HMIs, slow response or flickering can lead to operational errors or safety issues.
For most indoor applications, standard TFT LCDs provide sufficient performance. Wide temperature displays are primarily needed for environments that experience extremes or rapid temperature changes.
Standard vs Wide Temperature TFT LCDs
Choosing the right TFT technology is key for balancing cost, performance, and reliability. Here’s a closer look:
| Type | Advantages | Considerations | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| a-Si | Cost-effective, reliable, widely available | Lower mobility under extreme temperatures, slower response | Basic industrial panels, indoor HMIs |
| LTPS | High mobility, fast response, high-resolution support | Higher cost, more complex manufacturing | Automotive dashboards, premium industrial displays |
| IGZO | Low leakage, high temperature stability, low power consumption | More complex fabrication, cost slightly higher than a-Si | Outdoor displays, low-power IoT devices |
| LTPS/IGZO Hybrid | Balanced speed, power efficiency, and temperature stability | Higher manufacturing complexity | Automotive and industrial wide temperature applications |
It’s important to remember: the best display is the one that fits your application, not necessarily the one with the widest temperature range.
When Wide Temperature Displays Are Useful

Wide temperature TFT LCDs are designed for challenging conditions. They excel in scenarios where devices experience extreme heat, cold, or rapid temperature changes:
- Automotive Dashboards: Vehicles left outdoors in winter mornings or summer heat require screens that remain responsive and visible.
- Industrial HMIs: Panels in factories or outdoor production lines often face high ambient temperatures and direct sunlight.
- Outdoor Terminals: Information kiosks, marine navigation displays, and military screens operate year-round in unpredictable weather.
- Medical Portable Devices: Some portable imaging or monitoring devices are used in field hospitals or mobile clinics where temperature conditions vary widely.
While wide temperature displays offer advantages in these situations, they are often more expensive. For controlled indoor environments, a standard TFT LCD is sufficient and more cost-effective.
Key Considerations When Selecting a TFT LCD
When choosing a TFT LCD for your project, focus on these practical factors:
- Operating Temperature: Determine if your environment requires standard or wide temperature capabilities.
- Brightness & Sunlight Readability: Critical for outdoor displays or high-ambient-light applications.
- TFT Technology: Consider a-Si, LTPS, IGZO, or hybrid architectures based on mobility, power consumption, and thermal stability.
- Power Consumption & Thermal Management: Ensure LED backlight stability and system reliability under extreme temperatures.
- Compliance & Reliability: Certifications may be needed for automotive, industrial, or medical-grade displays.
- Interface and Resolution: The choice between RGB, LVDS, or MIPI interfaces affects integration and performance.
- Long-Term Performance: Consider aging of LEDs and TFTs under your operating temperature range.
The ultimate goal is to match the display to the real-world application, rather than simply choosing the highest-rated specs.
Optimizing TFT LCDs for Extreme Conditions
Even wide temperature displays benefit from careful design and optimization:
- Cold Start Optimization: Special liquid crystal formulations and low-temperature activators reduce slow response in sub-zero conditions.
- High-Temperature Stability: High-efficiency LEDs, temperature-compensated driver circuits, and proper thermal design maintain brightness and contrast.
- Hybrid TFT Architectures: LTPS/IGZO hybrids balance speed, low power consumption, and temperature stability for automotive and industrial applications.
- Thermal Management Techniques: Passive solutions like heat-conductive materials and optimized PCB layout, or active solutions like micro-fans and thermoelectric coolers, improve system reliability.
- Flexible Substrates: In some applications, flexible substrates and low-temperature printing can help tolerate thermal stress.
Common Misconceptions About Wide Temperature TFT LCDs
Many assume that a wide temperature rating always guarantees better performance. However:
- Wide temperature TFTs do not automatically mean faster response in standard conditions.
- For indoor or controlled environments, wide temperature displays may increase cost without noticeable benefit.
- Power efficiency may vary; sometimes standard TFT LCDs consume less energy in mild environments.
FAQ – Standard vs Wide Temperature TFT LCDs
Q: Do all applications need wide temperature displays?
A: No. Standard TFT LCDs are sufficient for indoor or controlled environments. Wide temperature screens are recommended for extreme or highly variable conditions.
Q: Why do LCDs respond slower in cold environments?
A: Low temperatures thicken the liquid crystal, slowing molecular reorientation. Optimized formulations can improve cold start performance.
Q: Which TFT technology works best for automotive displays?
A: LTPS or LTPS/IGZO hybrid TFTs provide high mobility and temperature stability. Selection should consider cost, power consumption, and integration requirements.
Q: How can LED backlight performance be maintained in extreme conditions?
A: Use high-efficiency LEDs, temperature-compensated driver circuits, proper thermal design, and cooling solutions if necessary.
Q: Can wide temperature displays operate in all outdoor conditions?
A: Wide temperature TFT LCDs cover extreme heat and cold, but factors like humidity, vibration, and direct sunlight exposure also affect performance and should be considered in the system design.
Conclusion
Wide temperature TFT LCDs are essential for certain automotive, industrial, outdoor, and specialized medical applications. However, the right display always depends on your specific environment and use case. Understanding the effects of temperature, TFT technologies, thermal management, and application requirements ensures reliable performance, cost-efficiency, and longevity. By choosing thoughtfully, you can achieve optimal display performance without unnecessary expense.