Introduction: Why Increasing LCD Brightness Matters in TFT LCD Display
TFT LCD display is non-emissive display. How to increase display brightness is entirely determined by two factors:
-
how much light the backlight module can generate, and
-
how efficiently this light passes through the LCD panel structure.
Poor brightness directly impacts readability and user experience in industrial, outdoor and high-ambient-light settings. Thus, achieving a high brightness LCD or sunlight readable LCD display mainly focuses on two directions:
-
generating more efficient backlight output, and
-
reducing optical loss along the light path.
Among all influencing factors, backlight design is the most critical and effective way to increase display brightness. This article focuses on backlight optimization while also covering supporting panel-level and system-level considerations.
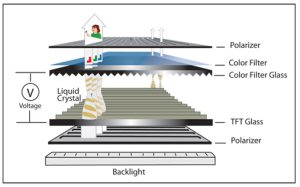
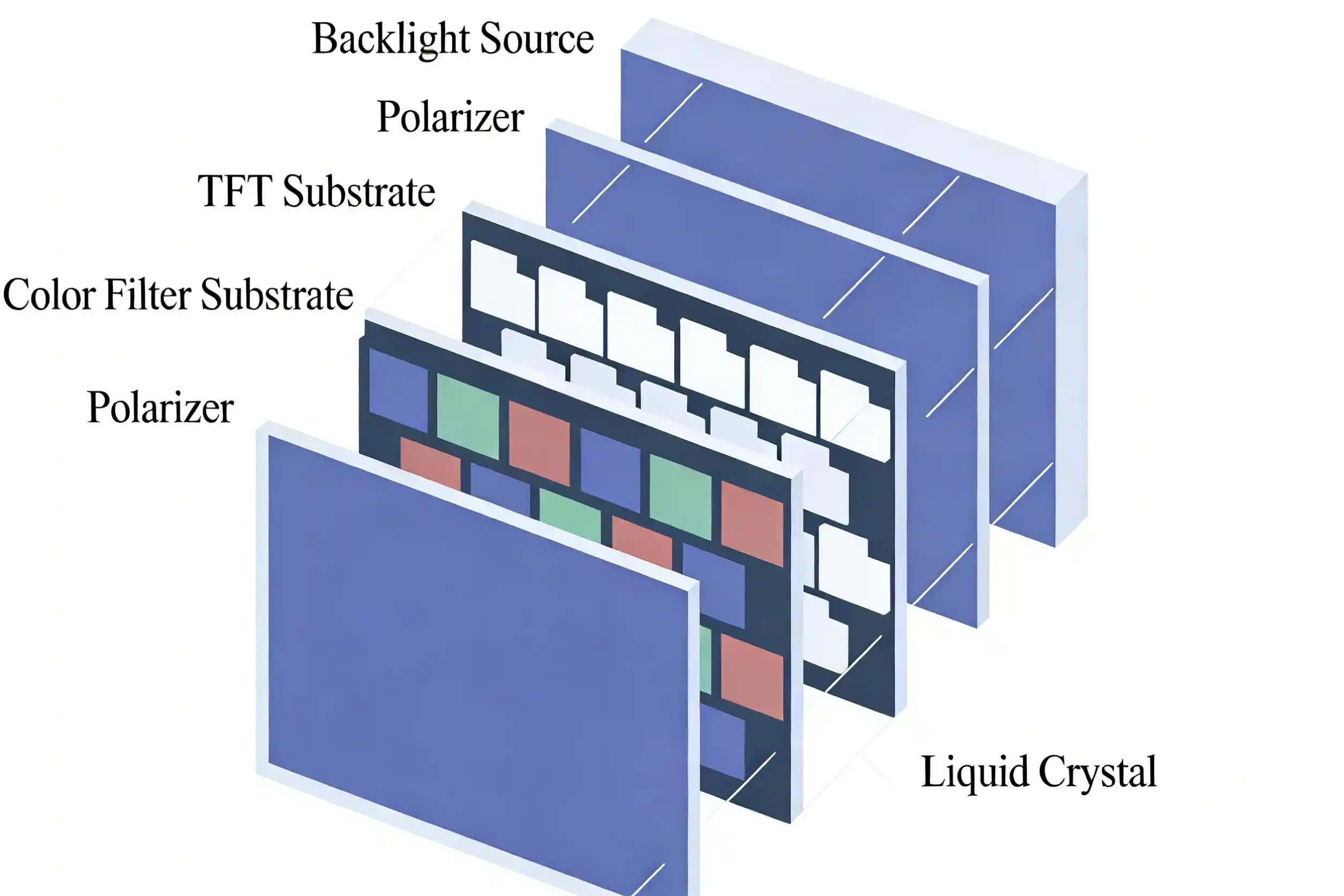
Learning the Backlight Structure of TFT LCD Display
The backlight of a typical TFT LCD display is made up of a number of layers that are crucial in the manner in which LCD brightness is determined:
-
LED Light Source Layer: Provides the primary illumination. Depending on the brightness requirements, single-chip LEDs or dual-chip LEDs are regularly available.
-
Light Guide Plate (LGP): Scattered light evenly over the display space providing the light to be even.
-
Optical Film Layers: Include diffuser films, brightness enhancement films (BEF), and reflectors to improve light efficiency and uniformity.
-
Heat Dissipation: Maintains LED stability and lifespan under high brightness operation.
It is necessary to maximize every character of the backlight in order to attain a high brightness LCD which is not only efficient, but also reliable.
Backlight Optimization – The Core to Increase LCD Brightness
1. Increasing LED Luminous Output per Unit to Enhance Display Brightness
The most direct way of enhancing display brightness is to improve the source of light itself.
-
Using higher-lumen LED chips
Refined semiconductor material (e.g. InGaN), refined chip layout (e.g. flip-chip LEDs) and enhanced packaging (e.g. refined thermal resistance) mean less thermal resistance and higher luminous efficiency with the same driving current. -
Increasing LED driving current (within reliability limits)
Higher current increases brightness but also accelerates heat generation and lumen degradation, making thermal design essential. -
Using dual-chip LEDs (two LED dies in one package)
-
Higher luminous output without increasing LED quantity
-
Suitable for compact backlight designs
-
Requires careful electrical matching and thermal management
-
Dual-chip LEDs are a mature and widely used solution for industrial high brightness LCD designs.
2. Increasing LED Quantity and Optimizing LED Arrangement in TFT LCD Display
-
Additional numbers of LEDs can be used to increase the total backlight output in direct-lit buildings.
-
Optimizing LED pitch and layout improves light coupling efficiency and brightness uniformity.
-
In embedded TFT LCD displays, designers have to trade off between brightness, power consumption, cost and mechanical thickness.

3. Backlight Driving Capability Improvement in Stable LCD Brightness
-
High-efficiency LED driver ICs support higher current and voltage requirements.
-
Correct adjustment of driver output to that of LEDs (single or twin chip) is necessary to achieve stability.
-
Proper design ensures stable brightness under prolonged high-brightness operation, reducing flicker and extending lifespan.
4. Optical Structure Optimization for High Brightness LCD Backlight
The optical films have a big role to play in the quantity of back light that is received by the viewer.
-
Brightness Enhancement Films (BEF)
Prism based BEFs focus scattered light in the forward viewing direction and cause an effective increase in on-axis brightness. Layers of BEF can be applied in case of the need of greater brightness. -
Diffuser films and plates
Optimized particle distribution improves light uniformity while minimizing absorption loss. -
High-reflectance reflector films
High-reflectivity materials recycle the non-utilized light which enhances overall backlight performance.
These optimizations are critical to sunlight readable LCD display performance.
Thermal Design for High-Brightness Backlights
High brightness inevitably leads to higher heat density.
-
High-power or dual-chip LEDs concentrate heat in localized areas
-
Metal backplates and optimized thermal paths are commonly used
-
Effective thermal management enables LEDs to be used with higher current and still, lifetime and constant LCD brightness.
Backlight Optimization: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the most effective way to increase display brightness?
A1: Optimizing the backlight, especially LED efficiency and optical films, is the most effective method to increase display brightness.
Q2: Are dual-chip LEDs suitable for industrial TFT LCD displays?
A2: Yes. Dual-chip LEDs are a mature solution for industrial high brightness LCD applications, provided that driver and thermal design are properly matched.
Q3: Can increasing LED current damage the display?
A3: Excessive current increases heat and accelerates LED degradation. Proper thermal design is essential for safe operation.
Q4: Do optical films really improve LCD brightness?
A4: Yes. BEF and reflector films significantly improve light utilization efficiency without increasing power consumption.
Additional Supportive Factors that influenced LCD Brightness in TFT LCD Display
1. LCD Panel Transmittance
-
Aperture ratio defines the amount of light which is allowed to pass through each pixel.
-
Advanced TFT processes (such as LTPS) and optimized pixel design improve transmittance
-
Liquid crystal materials and color filter transmittance directly affect optical efficiency
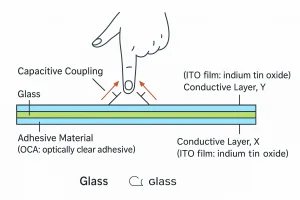
2. Touch Panel and Cover Glass Structure
-
Thinner cover glass reduces light absorption
-
Touch structures (GG, GFF, OGS) and optical bonding improve overall light transmission
3. System-Level and Software Optimization
-
PWM duty cycle adjustment controls backlight output
-
Gamma and contrast tuning improve perceived brightness
-
Software optimization complements, but does not replace, backlight hardware design
Applications of High Brightness LCD Display
-
Outdoor kiosks and information terminals
-
Industrial HMI and control panels
-
E-bike, vehicle mounted and transportation displays
-
Commercial and medical equipment used under strong ambient lighting
Conclusion: Achieving Reliable High Brightness TFT LCD Display for Industrial Applications
Backlight optimization is the most important aspect in order to enhance display brightness in a TFT LCD display with regard to LED efficiency, the structure design of optic and driving stability.
However, achieving high brightness is not only about output power. Thermal management and power efficiency play a key role in maintaining long-term brightness stability and product reliability. Adequate heat removal assists to avoid brightness decay, whereas, enhanced luminous efficiency (lm/W) allows a reduced brightness, power consumption, and system price.
With a well-designed backlight and controlled thermal performance, sunlight readable TFT LCD displays can reliably meet the demands of industrial and outdoor applications.