What is a Grey Spot on Phone Screen and Why Does it Matter?
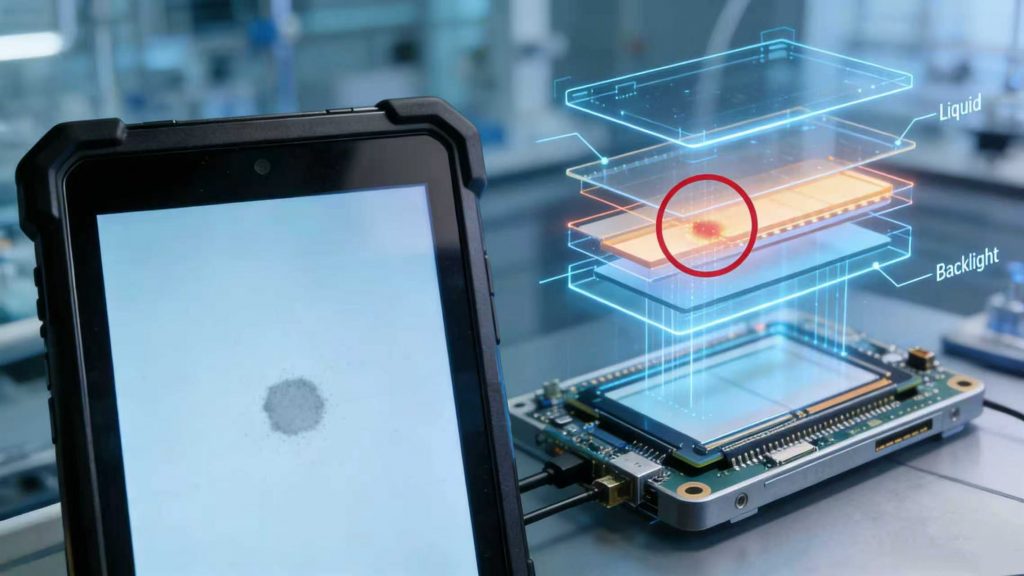
A grey spot on phone screen is a common visual anomaly that can range from a faint, cloudy patch to a distinct dark circle. This defect is a physical manifestation of damage occurring within the display panel’s layers—the LCD or OLED stack. Understanding the root cause is the first step toward prevention and repair. These spots are not random; they are the result of specific physical stresses or environmental failures that compromise the structural integrity of the display.
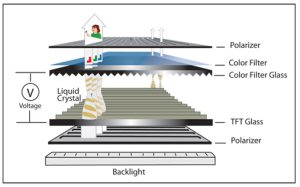
The appearance of this discoloration is a signal that the delicate internal structure of the display—which includes the polarizer, liquid crystal layer, thin-film transistors (TFTs), and backlight unit (BLU)—has been compromised. For consumer devices, it’s an inconvenience; for professional-grade equipment, it’s a critical failure that demands a deeper technical understanding.
Mechanical Failure: The Root of Display Module Stress Damage
One of the most frequent physical origins of the grey spot is mechanical strain, leading to
display module stress damage. This occurs when external force is applied unevenly to the screen assembly. This force can disrupt the alignment of the liquid crystals in an LCD or damage the delicate encapsulation layers in an OLED. Common culprits include excessive screw torque during mounting, tight enclosures, or constant vibration from heavy machinery.
The effect of mechanical stress is often localized. For example, a sharp impact can cause micro-cracks in the glass substrate or the underlying circuit board, leading to a localized pressure point that permanently alters the optical properties of the display material. This type of failure is particularly insidious because the initial impact may not cause immediate failure, but the resulting internal strain leads to a grey spot weeks or months later. For more on designing against such forces, see our blog on rugged structural design.

Mitigating Display Module Stress Damage for Long-Term Display Module Reliability
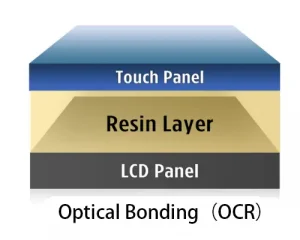
Preventing display module stress damage is crucial for maintaining long-term display module reliability. This involves using protective cases, avoiding direct pressure on the screen, and ensuring that any device assembly uses proper torque specifications. For industrial-grade devices, manufacturers often use specialized mounting frames and shock-absorbing materials to distribute force and prevent this type of structural failure. The use of full optical bonding, where the cover glass is directly adhered to the display panel, also helps to distribute external pressure more evenly, significantly reducing the risk of localized strain.
Environmental Factors: Other LCD/OLED Grey Spot Causes
Beyond mechanical stress, environmental factors are significant LCD/OLED grey spot causes. The two main culprits are moisture and heat. Moisture ingress—often through compromised seals—can cause corrosion of internal electrical components or chemical breakdown of the polarizer film, resulting in a cloudy grey patch. Similarly, excessive heat (thermal hotspots) can cause the internal layers to delaminate or warp, leading to permanent discoloration.
The display stack is a complex sandwich of materials, each with a different Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE). When exposed to rapid temperature changes, the differential expansion and contraction can pull the layers apart, creating air gaps or localized stress that manifests as a grey spot. Understanding the role of
Optical Bonding in preventing moisture ingress is key to environmental protection.
The Role of Moisture in LCD/OLED Grey Spot Causes
Moisture-related LCD/OLED grey spot causes are particularly prevalent in high-humidity or outdoor environments. When water vapor penetrates the display stack, it can lead to a phenomenon known as “mura” or non-uniformity. This is often exacerbated by temperature cycling, which causes the internal components to expand and contract, pulling moisture further into the display layers. The use of high-quality gaskets and specialized sealing materials, often rated to IP67 or IP68 standards, is essential to block the ingress of water vapor and maintain the integrity of the display’s internal environment.
Thermal Hotspots and Industrial Display Module Defects
The pursuit of high brightness and compact design often introduces the challenge of thermal management. Excessive, localized heat—or a “thermal hotspot”—accelerates the degradation of the display’s organic and polymeric materials. This thermal stress permanently alters the material structure, resulting in a permanent grey or yellow stain.
Data Point: The 10°C Difference
|
Metric
|
Standard Operating Temp (25°C)
|
Elevated Temp (35°C)
|
Impact on MTBF
|
|
Polarizer Degradation Rate
|
Baseline (1x)
|
1.5x
|
Accelerated
|
|
Liquid Crystal Viscosity
|
Optimal
|
Reduced
|
Potential for image sticking
|
|
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
|
100%
|
Reduced by up to 40%
|
Critical
|
|
Thermal Hotspot Risk
|
Low
|
High
|
Compromises Display Module Reliability
|
This issue is amplified in specialized equipment, where industrial display module defects due to heat can lead to mission-critical failure. Proper thermal management design involves using efficient heat sinks, thermal pads, and optimizing the layout of heat-generating components like the backlight LEDs and driver ICs to ensure uniform heat dissipation across the entire panel surface.
Summary of Grey Spot Causes and Preventing Industrial Display Module Defects
In summary, the primary causes of the grey spot are physical: mechanical stress, moisture, and heat. Addressing these factors is key to achieving high display module reliability. Whether you are a consumer protecting your phone or an engineer designing a rugged device, understanding these root causes allows for informed decisions on protection and material selection.
The final, often overlooked, cause is manufacturing residue. Even microscopic dust or foreign particles trapped between the layers during assembly can create a pressure point or react chemically over time, leading to a visible grey spot. This is why high-quality display manufacturing must occur in ultra-clean environments (e.g., Class 1000 cleanrooms) and utilize 100% Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) to catch these minute flaws before the module is shipped.
Summary Table: Primary Defect Causes and Mitigation