Transflective vs Reflective LCD for Outdoor Devices
As demand for outdoor displays continues to grow, including smart handheld devices, industrial terminals, smart retail systems, and outdoor instrumentation, sunlight readability has become a key design consideration. Many devices on the market still use transmissive display with high-brightness backlighting to achieve sunlight-readable performance. This approach is effective, though it can increase power consumption and heat, an important factor for battery-powered or compact devices.
At the same time, transflective LCD displays and reflective LCD displays have emerged as valuable alternatives. Both technologies enhance outdoor visibility while reducing reliance on high-power backlights. Understanding the differences between them helps engineers choose the solution that best balances outdoor readability, power efficiency, and touch display integration for their specific application.
Quick Comparison at a Glance
- Transmissive display: Works well indoors; outdoor readability is achievable with a high brightness LCD display.
-
Transflective LCD display: Hybrid of transmissive and reflective modes; delivers good visibility both indoors and outdoors.
-
Reflective TFT display: Utilizes ambient light only, providing excellent sunlight readability with ultra-low power consumption.
This overview sets the stage for a deeper discussion of how each display type works and when to select the most suitable technology for a given application.
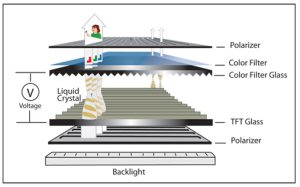
Transmissive LCD – The Most Common LCD Structure
A transmissive display relies entirely on its backlight. Light must pass through the liquid crystal layer to form the final image.
Key Characteristics:
-
Excellent color performance and high brightness
-
Ideal for indoor environments, HMIs, industrial equipment, vehicle dashboards, and general-purpose applications
-
Poor sunlight readability, ambient light reflection can wash out the screen unless using a high brightness LCD display
-
The most widely adopted structure (smartphones, tablets, industrial monitors, medical devices, automotive displays)
Relation to Other LCD Types:
-
A transflective TFT display builds upon transmissive architecture by adding a semi-reflective layer to improve outdoor visibility via ambient light reflection
-
A reflective TFT display removes the backlight entirely, relying solely on reflected ambient light to produce images, resulting in extremely low power consumption
Understanding transmissive vs transflective vs reflective TFT structures provides the basis for evaluating which one fits different outdoor or sunlight-readable applications.
Transflective TFT Display: Features, Advantages, and Applications
1. How a Transflective LCD Display Works
A transflective TFT display involves a semi-transmissive semi-reflective layer known as a transflector:
-
Indoors: the backlight provides brightness and color
-
Outdoors: the transflector reflects ambient light to enhance visibility
This hybrid design allows stable readability in both indoor and outdoor lighting conditions.
2. Advantages
-
High visibility in partially indoor/outdoor conditions
-
Lower energy consumption than high-brightness transmissive display
-
Reduced heat generation
-
Compatible with both resistive and capacitive touch displays
-
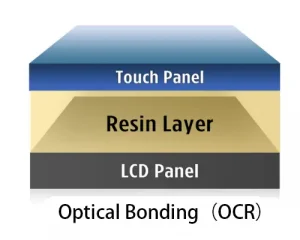
Optical bonding and anti-glare treatments further improve outdoor touch performance
3. Limitations
-
Slightly lower contrast compared to fully transmissive displays in very low light
-
Color saturation may be less vivid than transmissive high brightness LCD display
4. Typical Applications
-
Industrial handheld terminals
-
Outdoor POS systems
-
Field instruments and PDAs
-
Military and rugged tablets
-
Solar-powered devices
Reflective LCD Display: Features, Advantages, and Applications
1. How a Reflective LCD Display Works
A reflective TFT display replaces the backlight with a reflective layer:
-
Low light/indoors: visibility is limited
-
Bright sunlight/outdoors: ambient light is reflected, providing excellent readability
This design is optimized for outdoor use and low power consumption.
2. Advantages
-
Excellent readability under direct sunlight
-
Very low energy consumption
-
Minimal heat generation
-
Appropriate to always-on or battery-powered devices
3. Limitations
-
Poor visibility in low light or indoor environments
-
Usually monochrome or low-color, not ideal for high-graphics UI
-
Limited color and brightness flexibility
4. Typical Applications
-
Outdoor measurement instruments
-
E-paper alternatives and electronic labels
-
Fitness trackers and wearable devices
- Low-power IoT devices
Comparing Transflective vs Reflective LCD
To help visualize the differences between these two technologies, the table below summarizes key performance factors:
| Feature | Transflective LCD Display | Reflective LCD Display |
|---|---|---|
| Backlight | Optional / dimmable | None |
| Sunlight Readability | Excellent | Excellent (even stronger in direct sunlight) |
| Indoor Visibility | Good | Poor |
| Color Performance | Moderate | Limited / monochrome |
| Power Consumption | Low to moderate | Very low |
| Touch Display Integration | Excellent | Limited |
| Best Use Case | Indoor/outdoor devices, touch displays | Outdoor low-power devices, simple UIs |
-
Transflective LCD display offers a balanced solution suitable for most outdoor devices.
-
Reflective LCD display is ideal for ultra-low-power, sunlight-dominant applications.
-
Choosing between them depends on power budget, color needs, touch requirements, and expected environment.
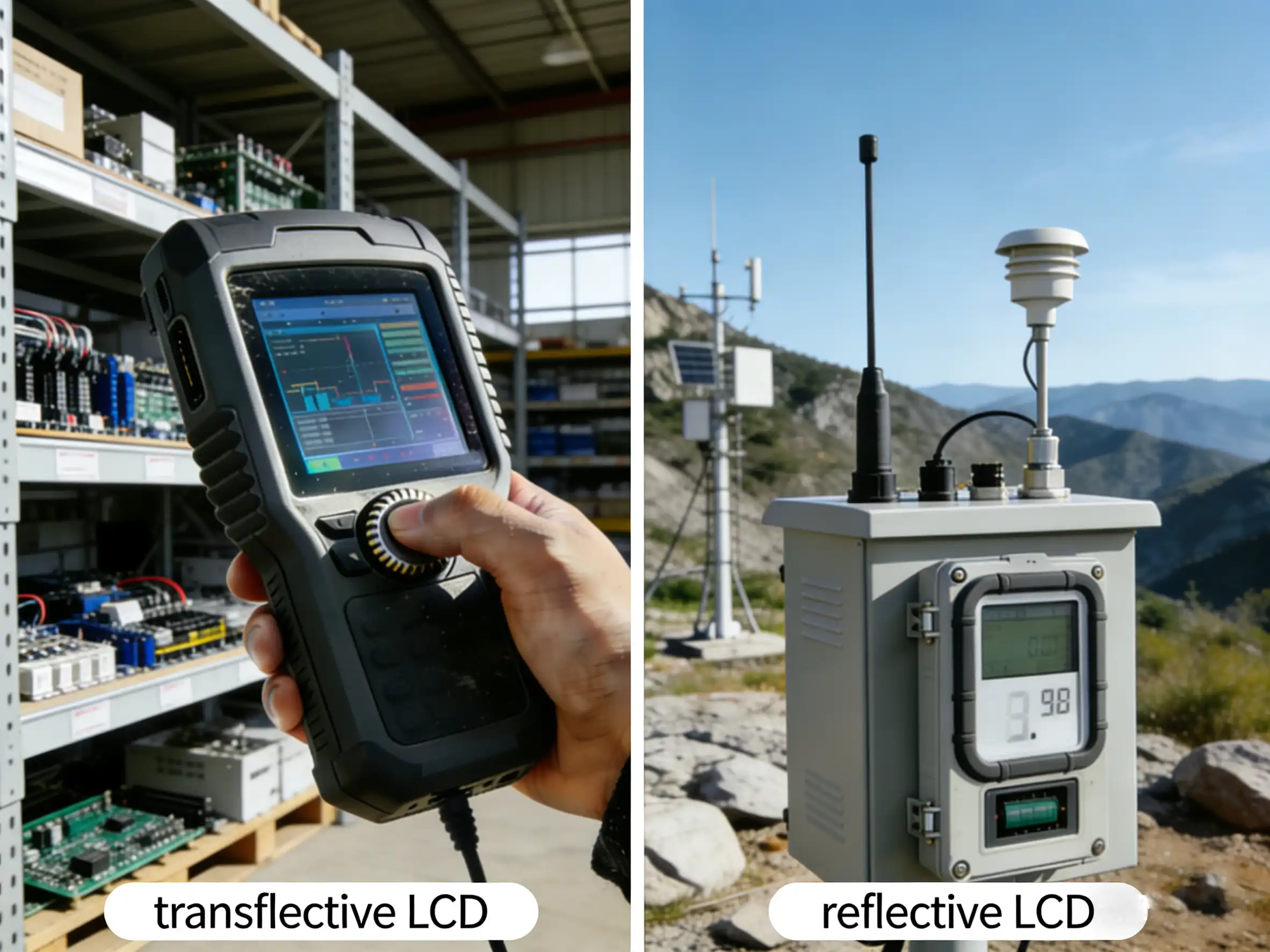

How to Choose the Right Display Technology for Your Device
When to Choose a Transflective TFT Displays
Select transflective LCD when your device:
-
Is used both indoors and outdoors
-
Needs color and moderate brightness
-
Needs lower power consumption than a high brightness LCD
-
Touch displays or interactive interfaces are involved
Ideal for industrial handhelds, tablets, POS, and field equipment.
When to Choose a Reflective LCD Display
Choose reflective LCD if you need:
-
Ultra-low power
-
Good visibility under sunshine
-
Simple monochrome or low-color UI
-
Prolonged battery life or solar powered
Ideal for meters, labels, wearables, and IoT devices.
Conclusion
Each display technology offers distinct advantages for outdoor and industrial applications, and understanding their differences helps engineers make the right choice:
-
Transflective displays provide the best balance between indoor color performance, outdoor readability, and moderate power consumption, making them ideal for mixed-environment devices.
-
Reflective displays offer excellent sunlight readability with very low power consumption, which is highly appropriate in simple interfaces, always-on displays and very low-power products.
-
Transmissive displays, especially when paired with a high brightness LCD display configuration, remain a practical and widely used option for devices that prioritize vivid colors and primarily indoor usage, while still achieving sunlight readability when needed.
By evaluating these strengths and limitations, developers can select the display technology that ensures the best overall user experience, energy efficiency, and long-term reliability for their specific outdoor application.