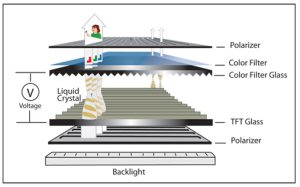
Introduction – The Rise of Round LCD and TFT Displays
Round LCD displays are no longer confined to wearables. Today, they are showing up in smart thermostats, medical terminals, and industrial knobs—driven by demand for compact, modern interfaces.
Models like Rocktech’s 1.3-inch Round LCD and 3.4-inch modelsare already used in smart home panels and wearables. Additional sizes such as 2.1” and 4.0” are also available on request.
Why Are Round Displays Gaining Popularity?
Unlike traditional rectangular screens, round LCDs provide a more organic and intuitive appearance, making them ideal for wearables, automotive dashboards, and modern HMI devices. This shift is not just about looks — circular screens support new interaction models, such as rotary knobs and radial menus, which are more aligned with the ergonomics of physical interfaces.
What Is a Round Display? Clearing Up Misconceptions
A round display typically refers to a circular TFT LCD panel that may or may not include touch functionality. Some developers assume these are simply cropped rectangular screens, but in fact, they are uniquely engineered with circular active display areas, custom backlight modules, and curved polarizers to ensure image consistency across the entire surface.
Another common misconception is that round displays are limited in resolution or clarity. On the contrary, many modern round LCD displays now support high-resolution IPS panels with full color, wide viewing angles, and touch capabilities — all while maintaining a small footprint.
Benefits of Round UI Designs in Embedded Devices
In embedded applications, round user interfaces offer several advantages:
- Design Differentiation: A round screen immediately makes your product stand out from the crowd.
- Intuitive Navigation: Circular layouts pair well with physical knobs, enabling seamless scrolling and interaction.
- Space Efficiency: Many devices, such as thermostats and meters, naturally suit a circular layout within a compact form factor.
For developers looking to modernize their product designs or explore new interaction paradigms, integrating a round TFT display is a powerful step toward innovation.
Round LCD Display Technologies: TFT, IPS, and Beyond
The world of round LCD displays is expanding rapidly, with advancements in panel technology enabling better performance, broader viewing angles, and richer color representation. In industrial, medical, and smart home applications, choosing the right display type is crucial for both user experience and long-term reliability.
What Types of Round LCD Displays Are Available?
Modern round LCD modules come in several technical variants, each tailored to specific application requirements. The most common types include:
- Round TFT LCD: A thin-film transistor liquid crystal display with active matrix driving, ideal for rich color and fast response.
- Round IPS Display: In HVAC control panels or automotive knobs, IPS ensures critical data remains visible even from side angles, with viewing angles up to 178° and brightness exceeding 800 nits.
- Transflective Round LCD: Designed for outdoor use, these panels reflect ambient light to boost readability in sunlight.
OLED is generally avoided in industrial round displays due to its shorter lifespan and image retention issues.
Why Choose IPS Technology for Round Displays?
In-plane switching (IPS) has become the preferred display technology for applications requiring color accuracy and wide viewing angles. In round displays, where users may approach the screen from different angles — such as in automotive knobs, thermostats, or smart meters — IPS ensures the content remains visible and consistent from every direction.
IPS-based round TFT displays also offer enhanced image stability, making them ideal for industrial environments and mission-critical interfaces. Their typical viewing angles reach up to 178° horizontally and vertically, with contrast ratios of 800:1 to 1000:1 and excellent sunlight readability when paired with high brightness backlights.
Note: While OLED technology offers excellent contrast and flexibility, it is rarely used in industrial round displays due to limited lifespan and image retention issues. TFT-based solutions remain the dominant choice for long-life embedded applications.
Optional Features and Customization Options
When selecting a round LCD module, engineers and designers can tailor several features based on the project’s functional and mechanical needs:
- Touch Function (CTP): Capacitive touch support for intuitive UI control.
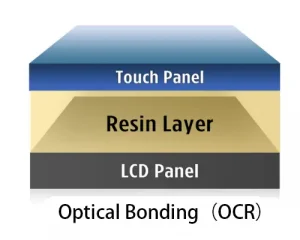
- Bonding Types: Choose between air bonding (cost-effective) and optical bonding (better sunlight readability and durability).
- FPC Interface Options: Common interface types include SPI, RGB, MIPI, or MCU — selectable based on system architecture and resolution requirements.
Whether you’re developing a smart home controller, a wearable device, or a control knob for an industrial system, modern round LCD displays offer the technology and customization flexibility to meet both visual and mechanical design challenges.
Where Are Round LCDs Used? From Wearables to Knob Displays
Thanks to their aesthetic appeal and functional flexibility, round LCD displays have found their way into a wide variety of embedded applications. Whether it’s for consumer electronics or industrial systems, these circular screens offer a modern alternative to traditional square or rectangular displays.
Smart Wearables: Compact Screens with High Pixel Density
Round LCDs are widely adopted in smartwatch and wearable devices, where space is limited and visual design is paramount. These displays typically feature high pixel densities (PPI), capacitive touch integration, and ultra-low power consumption — all within a 1.0 to 1.6-inch diameter form factor. Their symmetrical design not only improves aesthetics but also enhances readability in any orientation.
Smart Home & Appliance Interfaces: Circular UI Meets Intuitive Control
Home automation systems and smart kitchen appliances are increasingly adopting round displays as a UI centerpiece. Thermostats, induction cookers, smart showers, and air purifiers benefit from the circular layout, which naturally aligns with rotary control interfaces and simplifies on-screen navigation.
Knob Display Integration: A Low-Cost, High-Impact Solution
Knob displays—featuring a circular TFT with capacitive touch and a rotary encoder—are gaining traction in smart appliances and fitness devices. With UART/SPI connectivity and compact size, they simplify system integration while offering a modern UI.
Portable Medical and Industrial Terminals
In the medical and industrial fields, round TFT LCDs are used in compact diagnostic devices, handheld instruments, and rugged outdoor terminals. Their small footprint, durable structure, and optional high brightness backlighting make them ideal for fieldwork, emergency response, or point-of-care applications.
When combined with industrial-grade touch sensors and reinforced glass, these displays ensure reliable performance under harsh conditions, including water, dust, and strong ambient light.
As embedded applications demand more compact yet stylish interfaces, round LCDs — including advanced knob display designs — are redefining the way users interact with machines across multiple industries.
How to Choose the Right Round LCD Display for Your Product
Selecting the most suitable round LCD display for your embedded project requires a careful balance of display performance, interface compatibility, and mechanical constraints. Below are the key factors you should evaluate before choosing a module.
Key Parameters to Consider
- Resolution: Match the pixel count to your UI detail requirements and controller capabilities.
- Interface: Choose between SPI, RGB, MIPI, or LVDS depending on your mainboard I/O and data rate needs.
- Display Size: Most round displays range from 1.0” to 3.5”. Size impacts both visual effect and enclosure design.
- Backlight Brightness: If outdoor or high ambient light usage is required, aim for ≥500 nits.
- Power Supply: Confirm that the panel’s logic and backlight voltage requirements match your system’s power rail.
Recommended Configurations for Common Applications
| Application | Display Size | Interface | Touch | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Wearables | 1.3″ ~ 1.6″ | SPI / MIPI | CTP (Optional) | Low power, high PPI, compact design |
| Knob Display / Smart Home | 2.0″ ~ 2.4″ | SPI / RGB | CTP + Encoder | Rotary interaction with compact UI |
| Industrial Terminal | 2.4″ ~ 3.5″ | RGB / LVDS | Optional | High brightness, wide temperature range |
If you’re using a rotary knob + CTP combination, leave at least 5mm of internal housing space behind the module to ensure encoder alignment and thermal airflow. By aligning technical specs with user experience goals and enclosure constraints, you can ensure a seamless integration of round TFT displays into your embedded product.

Conclusion – Round LCD Displays Empower the Future of Embedded HMI
Round LCD displays are rapidly reshaping the way we think about embedded human-machine interfaces. Their ability to combine aesthetics, functionality, and versatility makes them an essential element of modern product design — from smartwatches to industrial knobs and portable terminals.
Why Round LCDs Are a Future-Proof Choice
The shift from boxy rectangles to dynamic circular displays is not just a design trend — it’s a response to real-world user interaction needs. Whether it’s enhancing visibility in wearables, creating intuitive rotary interfaces in home appliances, or building stylish yet rugged industrial terminals, round LCD modules provide the flexibility developers need.
What to Expect in the Future
- More custom ID designs made possible by flexible glass and optical bonding techniques.
- Integration with multi-mode inputs like gesture, touch, and encoder-based control.
- Wider adoption in IoT and edge computing devices due to low-power high-efficiency panel technology.
Final Tips for Developers
As round displays become increasingly common, developers should stay mindful of the following:
- MCU/GPU Compatibility: Make sure your SoC or controller can handle circular screen resolutions and aspect ratios.
- Firmware Optimization: UI frameworks like LVGL or QT5 may need radial interface libraries or custom graphics logic.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Source from trusted partners with stable long-term production capabilities and support.
Round LCDs offer more than just aesthetics — they enable compact, intuitive, and differentiable designs. As interface expectations grow, circular displays are becoming a practical foundation for modern embedded systems.