Introduction to Resistive Touch vs Capacitive Touch for TFT LCD Displays
The evolution of TFT LCD displays has dramatically reshaped how users interact with digital devices. From industrial machines to medical devices and consumer electronics, touch-enabled displays are now the cornerstone of intuitive user experiences. Within this evolution, two primary technologies dominate the touch interface landscape: resistive touch panels (RTP) and capacitive touch panels (CTP).
Choosing between resistive touch vs capacitive touch is more than a technical decision—it’s a strategic one that impacts performance, durability, cost, and user satisfaction. This article explores the differences between these two technologies, providing practical guidance for manufacturers and system integrators using TFT LCD displays.
Principles and Use Cases of Resistive Touch vs Capacitive Touch

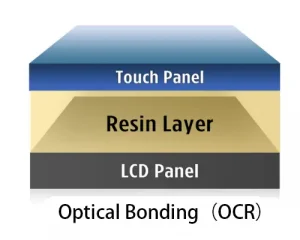
Resistive-Touch-vs-Capacitive-Touch
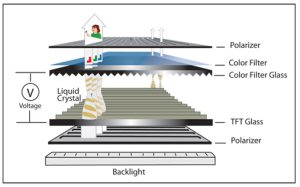
Touch technology in TFT LCD panels relies on two major types: resistive TFT and capacitive TFT. Both serve the same purpose—enabling user input via direct contact—but differ significantly in principle, usability, and environment suitability. For general background, you can refer to this comprehensive overview of touchscreen technologies.
What is a Resistive TFT Touch Panel?
How Resistive Touch Works
Resistive touch panels operate based on pressure. When the screen is pressed, two conductive layers connect, sending coordinates to the controller. It responds to any object—stylus, gloved finger, or bare hand—making it ideal for industrial and outdoor use.
Benefits and Use Cases of Resistive Touch
Advantages:
- Compatible with gloves and styluses
- Works in wet or dirty environments
- Lower production cost
Applications:
- Industrial equipment interfaces
- ATMs and public kiosks
- POS systems
What is a Capacitive TFT or Projected Capacitive Touch Screen?
How Capacitive Touch Works
Capacitive TFT technology senses the electrostatic field of a human finger. In projected capacitive touch screens (PCAP), electrodes form a grid that detects this disturbance and translates it into precise input without needing pressure.
Benefits and Use Cases of Capacitive Touch
Advantages:
- Supports multi-touch and gesture controls
- High light transmittance for better clarity
- Sleek and responsive user experience
Applications:
- Smartphones and tablets
- Automotive displays
- Smart home controls
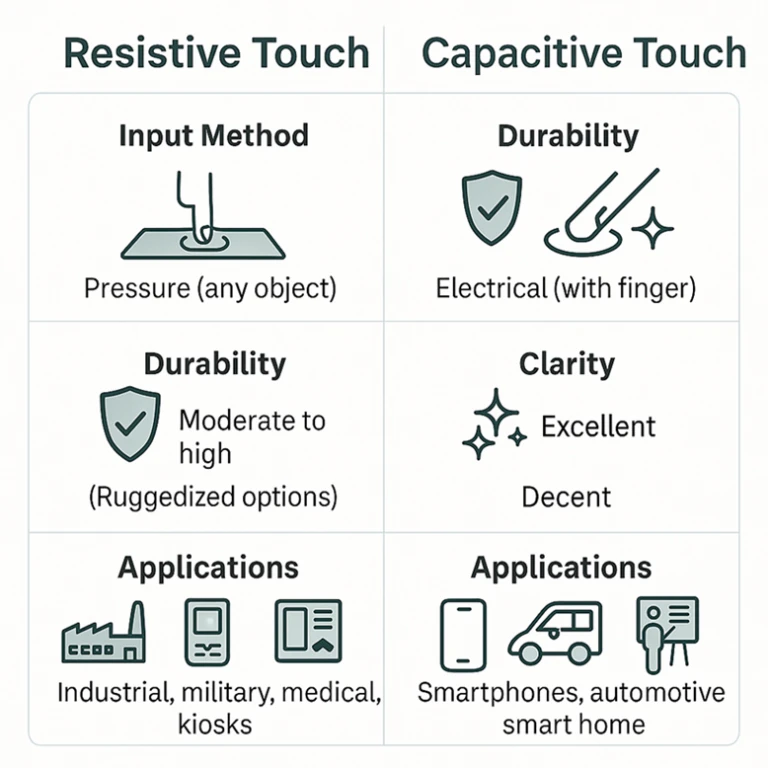
Core Comparison of Resistive Touch vs Capacitive Touch for TFT LCD Displays
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Resistive TFT | Capacitive TFT / PCAP |
| Input Method | Finger, stylus, glove | Bare finger (customizable for glove) |
| Multi-Touch | Limited (usually single-touch) | Supported |
| Durability in Harsh Conditions | High | Customizable with rugged glass |
| Display Clarity | Moderate (~75–85% light transmittance) | High (~90% or more) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Environmental Flexibility and Customization
While resistive TFT displays are naturally durable, capacitive TFT displays can now match many of these qualities. Modern projected capacitive touch screens allow custom ICs that enable glove operation, moisture tolerance, and stylus support. Cover lenses can be toughened or thickened to withstand industrial use while maintaining excellent touch sensitivity and clarity. Please refer to Rocktech Custom Touchscreen Displays.
Applications of Capacitive TFT vs Resistive TFT LCD Displays
Industrial and Medical Use
Resistive touch is favored in rugged environments requiring high reliability. Capacitive touch is gaining ground due to its adaptability and enhanced UI responsiveness with proper customizations.
Consumer Electronics and Automotive
Projected capacitive touch screens dominate this segment thanks to their sleek appearance, high sensitivity, and gesture support, delivering the experience consumers expect.
Long-Term Supply and Custom Requirements
Resistive TFT is easier to adapt for small batch, long-life applications. Capacitive TFT displays benefit from economies of scale and rapid evolution, especially in high-volume markets.
Resistive-Touch-vs-Capacitive-Touch
Will Capacitive TFT Replace Resistive Touch Technology?
Although projected capacitive touch screens are becoming standard in consumer products, resistive TFT remains vital in industrial and specialty sectors. The ability of capacitive TFT to support gloves, moisture, and custom cover glass via tailored ICs shows promise. Yet, RTP continues to dominate where cost, simplicity, and environmental durability are critical.
The future likely holds coexistence: capacitive touch for modern, interactive designs; resistive touch where robustness and versatility are paramount.
Future Outlook for TFT LCD Touch Technologies
As industries continue to evolve, so do user expectations for display technology. Innovations in both resistive TFT and projected capacitive touch screens are closing performance gaps while opening new possibilities. For example, hybrid solutions combining pressure and capacitance are in development to offer the best of both worlds. In emerging markets, demand for ruggedized displays with custom sensitivity is driving further development in both technologies.
Additionally, TFT LCD displays are increasingly being integrated into AI-driven interfaces, wearable devices, and smart automation systems. These applications demand flexible, highly responsive, and durable touch input—pushing suppliers to continue innovating in both resistive and capacitive domains.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Touch Technology for Your TFT LCD Display
In the debate of resistive touch vs capacitive touch, no one-size-fits-all answer exists. Decision-makers must consider budget, environment, expected user behavior, and long-term maintenance.
- Choose resistive TFT for rugged, glove-usable, cost-sensitive devices.
- Choose capacitive TFT or projected capacitive touch screens for interactive, user-friendly, and aesthetically driven interfaces.
Both technologies are integral to modern TFT LCD displays—understanding their capabilities will help ensure optimal integration and user satisfaction.