What is IPS display? IPS (In-Plane Switching) display technology is a widely adopted LCD panel technology used in applications that demand precise color rendering and superior viewing angles. An IPS display stands out from other screen types due to its stable performance, especially in industrial and medical environments.
What is IPS Display Technology and How It Works in LCD Panels
IPS display technology is a type of TFT LCD (Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display). Unlike older TN (Twisted Nematic) panels that twist liquid crystals vertically, IPS panels align crystals parallel to the display glass. This lateral alignment reduces distortion and delivers superior optical performance across wider viewing angles.
History of IPS Displays and In-Plane Switching Panels
In-Plane Switching was developed by Hitachi in the mid-1990s as a solution to the poor color and angle performance of TN panels. Over the years, IPS panels have evolved with better contrast ratios, faster response times, and lower power consumption. Today, they are used extensively in professional-grade monitors, industrial screens, and medical devices.
How Does an IPS Display Work?
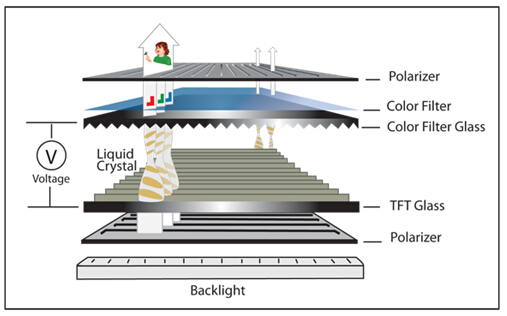
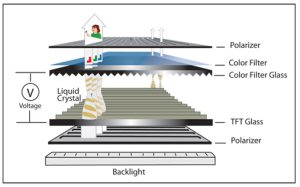
To understand how an IPS display works, it’s helpful to look at the basic structure of an LCD screen. In all LCD displays — including IPS, TN, and VA — a backlight sits behind a layer of liquid crystals and color filters. These crystals align in different ways to control how light passes through the screen and ultimately forms an image.
In traditional TN (Twisted Nematic) panels, the liquid crystals twist vertically to control light flow. However, this results in color shifting and poor image quality when viewed off-angle. In contrast, IPS displays use a technology called In-Plane Switching, where the liquid crystals align parallel to the screen’s surface. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate on the same plane, allowing light to pass through more consistently.
This parallel alignment of crystals enables IPS monitors to maintain uniform brightness and accurate color from wider viewing angles — typically up to 178 degrees horizontally and vertically. The design minimizes distortion and ensures a stable image, making IPS screens ideal for medical displays, control panels, and professional monitors that require consistent visibility across different positions.
If you view an IPS LCD from the side, you’ll notice far less color washout compared to TN screens. This predictable performance under varying angles is one of the reasons why IPS screen technology is preferred in industrial and diagnostic environments.
Key Advantages of IPS Panels
- Superior Color Accuracy: IPS panels deliver highly accurate and consistent color reproduction, ideal for medical displays, graphic design, and color-critical applications.
- Wide Viewing Angles: Maintain color and contrast up to 178° horizontally and vertically.
- Stable Contrast Levels: Excellent performance in environments with changing ambient light.
- Durability: Many industrial IPS screens are designed for 50,000 to 70,000 hours of continuous use.
IPS Display vs TN and VA Panels: A Technical Comparison
When choosing a display panel for your application, it’s important to understand the differences between IPS, TN, and VA technologies. Each offers distinct advantages and trade-offs, especially in terms of color accuracy, viewing angles, and performance. Here’s how these three LCD types compare:
| Feature | IPS | TN | VA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color Accuracy | Excellent | Poor | Good |
| Viewing Angles | 178° Wide | Narrow (90°–120°) | Moderate |
| Contrast Ratio | 1000:1 (typical) | 600:1 – 800:1 | Up to 3000:1 |
| Response Time | 4–5 ms | 1–2 ms | 4–8 ms |
| Price | Higher | Lower | Mid-range |
TN (Twisted Nematic) panels are best known for their low cost and fast response times, making them popular for budget gaming monitors. However, they suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, making them unsuitable for design or industrial applications.
VA (Vertical Alignment) panels offer superior contrast and deeper blacks than IPS, but often have slower response times and less accurate color. They are sometimes used in home TVs and mid-tier monitors.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) panels, on the other hand, provide the best balance of color fidelity, viewing angles, and long-term reliability. For professional environments—such as medical imaging, industrial HMIs, or smart home displays—IPS panels clearly outperform TN and VA in terms of visual quality and consistency.
If your project prioritizes image stability, accuracy, and wide-angle readability, IPS is the most reliable choice despite the slightly higher cost.
Common Applications of IPS Displays
- Industrial Control Panels: Reliable operation and high visibility in factory automation and HMI systems.
- Medical Devices: Accurate and stable color performance for diagnostics and patient monitoring.
- Smart Home Interfaces: Wide viewing angles for wall-mounted devices in modern home automation setups.
- Outdoor Signage: Combined with high brightness, IPS displays are readable even under direct sunlight.
How to Identify an IPS Screen
Many users ask: “How do I know if my display is IPS?” Signs of an IPS screen include:
- No color shift when viewed from the sides.
- Consistent brightness from any angle.
- More vibrant and accurate colors compared to TN panels.
IPS Display vs TFT LCD: What’s the Difference?
It’s important to note that IPS is a type of TFT LCD. While all IPS displays are TFT, not all TFT displays are IPS. The term “IPS display vs TFT” can be misleading — IPS is simply a premium variation of TFT technology, with better optical performance and wider use in industrial and professional fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is IPS display technology?
- IPS, or In-Plane Switching, is a type of LCD technology that uses parallel-aligned liquid crystals to offer wider viewing angles and better color reproduction.
- What does IPS mean on a monitor?
- It means the monitor uses IPS technology to deliver consistent brightness, color, and contrast, even when viewed off-center.
- Is IPS better than VA or TN?
- For color accuracy and viewing angles, IPS is better. VA has deeper contrast, while TN is faster and cheaper.
- What is IPS LCD used for?
- IPS LCDs are used in industrial control panels, medical monitors, tablets, smartphones, and professional displays.
- What is the difference between IPS and TFT displays?
- IPS is a subtype of TFT with improved performance. TFT refers to the transistor arrangement; IPS improves the optical characteristics.
Why Choose an IPS Display for Embedded and Industrial Systems?
Whether you’re designing a smart control panel, industrial monitor, or medical touchscreen interface, IPS displays provide the best combination of visibility, durability, and accuracy. Compared to TN or basic TFT options, IPS display panels maintain clarity even under wide angles or varying light conditions. That’s why more engineers are asking: what is IPS display technology, and how can I use it?
Conclusion
IPS panels have become the gold standard in display technologies where visual clarity and reliability are paramount. Their ability to deliver stable, accurate, and vibrant images under various operating conditions makes them the top choice for engineers, medical professionals, and industrial designers. Understanding what an IPS screen is and how it performs compared to other LCD types ensures smarter hardware decisions and long-term value for your projects.